
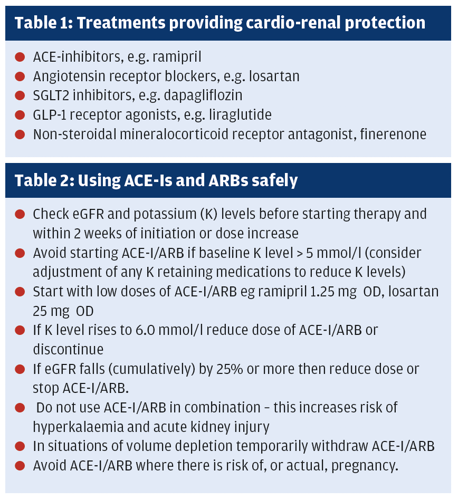
This second article on diabetic kidney disease looks at management of the condition (to read part one, click here). The key aims in managing DKD are to reduce the risk of cardiovascular (CV) events and slow the progression of renal disease1 and there are now several medications that offer both of these possibilities (see table 1).
Lifestyle
Bearing in mind the increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in DKD the healthy diet advised for people with diabetes is of great importance. Where appropriate, weight reduction, regular exercise and smoking cessation should be encouraged.1,2 Limiting salt intake is helpful in managing hypertension. In advanced DKD restriction of potassium and phosphate may be necessary, although by this stage the individual may well be under specialist care and have access to a renal dietician.
Register now for access
Thank you for visiting Independent Nurse and reading some of our premium content. To read more, please register today.
Register
Already have an account? Sign in here
